Emergency Management and Response
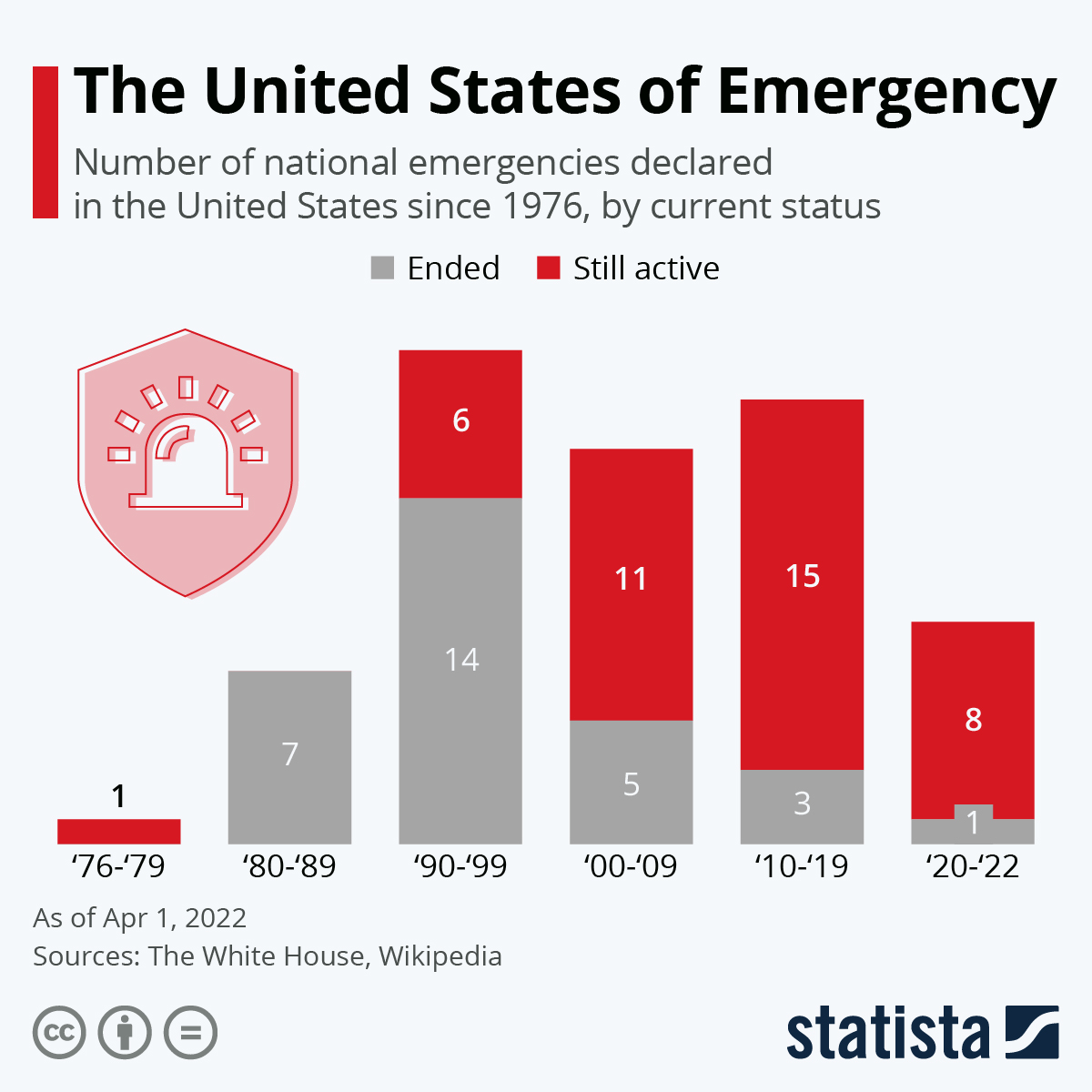
State of emergency – Emergency management encompasses a comprehensive framework of strategies and actions aimed at effectively managing and responding to emergencies. It involves four key phases: preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation.
The state of emergency, declared in response to the pandemic, has raised concerns about the erosion of civil liberties. However, some argue that it has also provided an opportunity to address long-standing issues, such as the power imbalance between homeowners associations (HOAs) and residents.
In Florida, for example, Governor DeSantis has signed a bill desantis hoa bill that gives residents more rights in HOA disputes. This could be a positive step towards restoring the balance of power and ensuring that the state of emergency does not become a permanent state of affairs.
During the preparedness phase, efforts focus on developing plans, training personnel, and acquiring resources to enhance readiness for potential emergencies. This includes conducting risk assessments, establishing emergency operations centers, and educating the public about emergency procedures.
Amidst the state of emergency, news of celebrity engagements provides a momentary distraction. Hailey Bieber’s engagement ring , a sparkling symbol of love and commitment, reminds us that life continues despite adversity. Yet, the underlying challenges remain, and the state of emergency serves as a sobering reminder of the need for vigilance and resilience.
Government Agencies and First Responders
Government agencies play a crucial role in emergency management, providing leadership, coordination, and resources. First responders, such as firefighters, police officers, and paramedics, are the frontline personnel responsible for immediate response and life-saving interventions during emergencies.
Challenges and Best Practices, State of emergency
Coordinating a comprehensive emergency response presents numerous challenges, including communication breakdowns, resource constraints, and public panic. Best practices for effective coordination involve establishing clear communication channels, utilizing technology for real-time information sharing, and fostering collaboration among all stakeholders.
Community Organizations
Community organizations play a vital role in emergency management by providing support and assistance to affected individuals and communities. They can assist with evacuation, shelter, and resource distribution, as well as provide emotional support and long-term recovery efforts.
Legal Implications and Constitutional Considerations: State Of Emergency

The declaration and implementation of a state of emergency are governed by a complex legal framework that seeks to balance the need for public safety with the protection of individual rights. This framework includes constitutional provisions, statutes, and case law that define the powers of government during an emergency and the limits on those powers.
One of the most important constitutional limitations on government power during a state of emergency is the due process clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. This clause requires that the government provide fair and reasonable procedures before depriving individuals of life, liberty, or property. During a state of emergency, the government may be able to take actions that would not be permitted under normal circumstances, but it must still comply with the due process clause. For example, the government may be able to detain individuals without a warrant during a state of emergency, but it must still provide them with a fair hearing as soon as possible.
Another important constitutional limitation on government power during a state of emergency is the First Amendment. This amendment protects the freedom of speech, press, assembly, and religion. During a state of emergency, the government may be able to restrict these freedoms to some extent, but it must do so in a way that is narrowly tailored to the specific threat posed by the emergency. For example, the government may be able to ban protests in certain areas during a state of emergency, but it cannot ban all protests outright.
The balance between public safety and individual rights during a state of emergency is a difficult one to strike. The government has a responsibility to protect the public from harm, but it must also respect the rights of individuals. The legal framework governing states of emergency is designed to help ensure that this balance is maintained.
Role of the Courts
The courts play an important role in ensuring that the government complies with the legal framework governing states of emergency. The courts can review the government’s actions to determine whether they are constitutional and reasonable. They can also issue injunctions to prevent the government from taking certain actions and can award damages to individuals who have been harmed by government actions.
Historical Examples and Case Studies
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/5KFEE3RMEBDZ7CZSULLSC3PWZM.jpg)
States of emergency have been declared throughout history in response to various crises. Some notable examples include:
- United States: The American Civil War (1861-1865) and World War II (1941-1945) led to the suspension of civil liberties and the implementation of martial law in certain areas.
- Germany: The Weimar Republic declared a state of emergency in 1933, which allowed the Nazi Party to seize power and establish a dictatorship.
- France: The Algerian War (1954-1962) prompted the French government to declare a state of emergency, granting the military broad powers to suppress the rebellion.
- India: The Emergency declared by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi in 1975 resulted in the suspension of civil rights, press censorship, and the detention of political opponents.
The effectiveness of emergency measures in addressing crises has varied widely. While some measures, such as increased security and restrictions on movement, may be necessary to maintain order and prevent violence, others, such as arbitrary arrests and detentions, have been criticized for violating human rights.
Lessons Learned
Past states of emergency offer valuable lessons for future planning:
- Legal Framework: Establish clear legal frameworks that define the conditions under which a state of emergency can be declared, the powers of the government during such a period, and the safeguards to protect civil liberties.
- Oversight and Accountability: Create independent oversight mechanisms to ensure that emergency powers are not abused and that the government is held accountable for its actions.
- Time Limits and Review: Set time limits for states of emergency and require regular reviews to assess their necessity and effectiveness.
- Respect for Human Rights: Even during emergencies, governments must respect fundamental human rights and ensure that emergency measures are proportionate and non-discriminatory.
Even in a state of emergency, sports can provide a momentary respite. The clemson vs coastal carolina game offered a welcome distraction, reminding us that even amidst turmoil, life goes on. But the state of emergency remains, a constant reminder of the challenges we face.
The state of emergency may have lifted, but the challenges we face remain. Like the lakers head coach who must navigate a season of adversity, we must find ways to adapt and overcome. The path ahead may be uncertain, but we must remember the resilience that has always defined us.
In the state of emergency, the presence of the invasive Asian water monitor has exacerbated the situation. These large lizards, native to Southeast Asia, have become a threat to native wildlife and pose a potential danger to humans. The government has taken measures to control the population, but the lizards continue to spread, raising concerns about the long-term ecological and safety implications for the state.